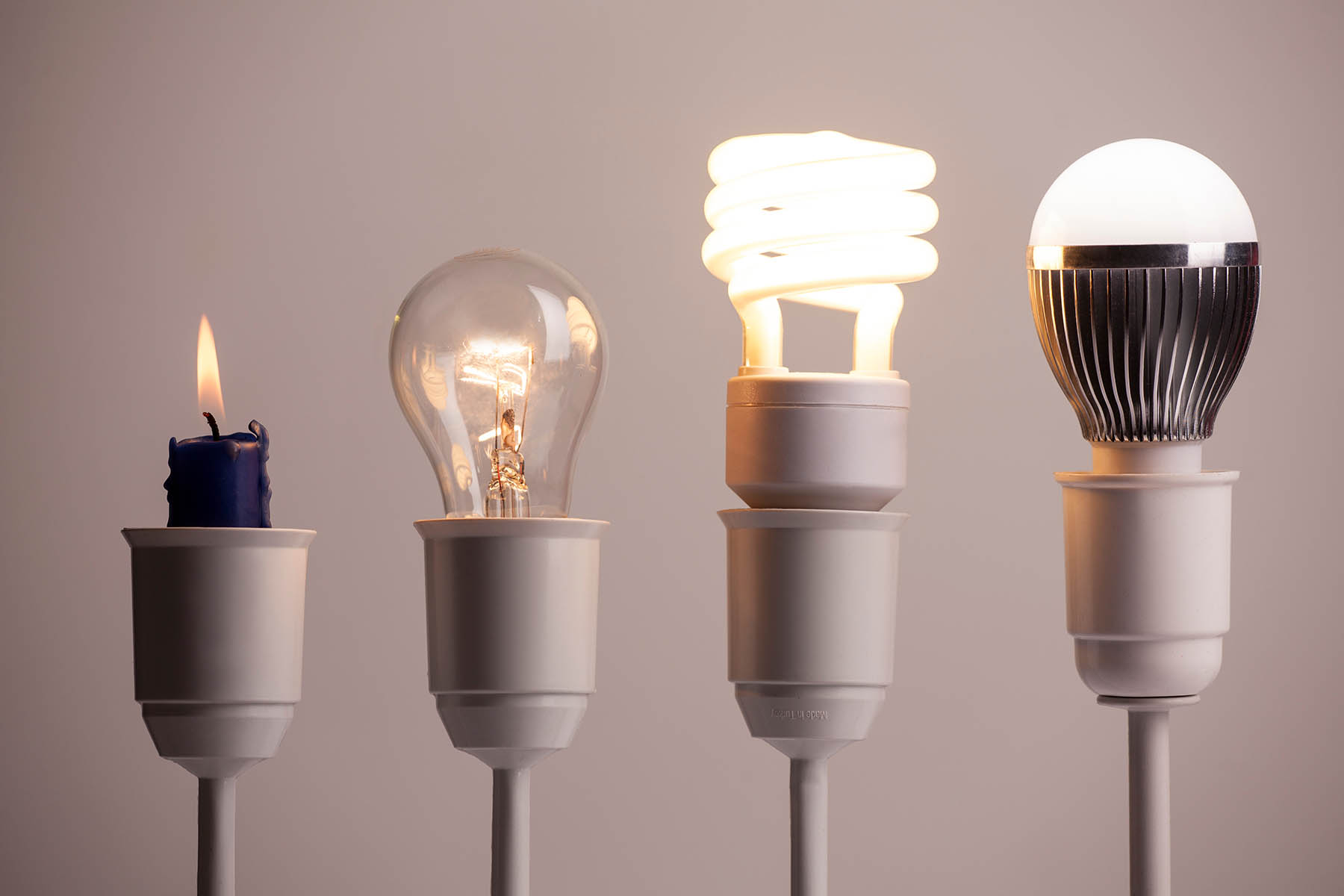
Lighting has undergone a profound transformation over the past century, evolving from inefficient incandescent bulbs to the highly efficient, long-lasting LED technology we rely on today. The evolution of LED lighting is a story of scientific breakthroughs, material innovations, and a shift toward sustainability. From its humble beginnings as a low-intensity indicator light to its current role as the primary source of illumination worldwide, LEDs have reshaped how we light homes, businesses, and public spaces.
This article explores the history, advancements, and future potential of LED lighting, detailing how it became the dominant lighting technology of the modern era.
The Origins of LED Technology: A Century-Old Discovery
The foundation for LED technology was laid in 1907 when British scientist H.J. Round first observed electroluminescence, the phenomenon where certain materials emit light when exposed to an electric current. However, at the time, this discovery had no immediate commercial application.
In 1927, Russian scientist Oleg Losev further explored electroluminescence and theorized the potential for solid-state lighting. Despite his research, the technology remained undeveloped due to limited understanding and material constraints.
For decades, scientists continued experimenting with semiconductor materials, gradually uncovering their ability to produce light under specific conditions. These early findings set the stage for the first practical LED development.
The 1960s and 1970s: The Birth of Practical LED Lighting
The breakthrough that led to the first functional LED light came in 1962 when Nick Holonyak Jr., an American engineer at General Electric, developed the first visible-spectrum LED—a red LED. Often called the “Father of the LED,” Holonyak’s invention laid the groundwork for future developments in solid-state lighting.
During the 1970s, additional LED colors, including green, yellow, and orange, were developed by researchers using new semiconductor materials. These LEDs were initially used for small indicator lights in electronic devices, calculators, and digital clocks. However, their low brightness and high cost limited their potential for general lighting applications.
The 1980s and 1990s: Breakthroughs in Efficiency and Color
The 1980s and 1990s were pivotal decades in the evolution of LED lighting, marked by significant advancements in brightness, efficiency, and color diversity. Researchers discovered how to improve the intensity of LEDs, making them brighter and more practical for expanded applications.
The Invention of Blue LEDs: A Game Changer
One of the most critical developments occurred in 1993, when Shuji Nakamura, along with Hiroshi Amano and Isamu Akasaki, successfully developed the first high-brightness blue LED using gallium nitride (GaN). This discovery was groundbreaking because blue LEDs enabled the creation of white LED light when combined with phosphor coatings.
With blue LEDs, manufacturers could now produce full-spectrum white light, making LEDs viable for general illumination. This innovation won Nakamura and his colleagues the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics, recognizing their contribution to revolutionizing global lighting.
The 21st Century: LEDs Become the Standard for Lighting
As LED technology advanced, it became brighter, more energy-efficient, and more affordable. By the early 2000s, white LEDs were being mass-produced, and their adoption in commercial and residential lighting began accelerating rapidly.
Key Milestones in LED Adoption
-
2008-2012: Many countries, including the United States and European nations, introduced policies to phase out incandescent bulbs in favor of energy-efficient LEDs.
-
2010s: The cost of LED bulbs declined dramatically, making them accessible to consumers on a large scale.
-
2015-present: LEDs surpassed fluorescent and incandescent bulbs as the most widely used lighting technology in homes, offices, streetlights, and automobiles.
With LED efficiency reaching 200 lumens per watt (lm/W)—far superior to incandescent (15 lm/W) and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) (60 lm/W)—the switch to LED lighting became an economic and environmental necessity.
How LED Lighting is Reshaping Modern Lighting Design
LEDs are not just more efficient; they have completely transformed lighting design by offering:
1. Compact, Flexible Lighting Solutions
Unlike traditional bulbs, LEDs are small, durable, and versatile, allowing integration into everything from ultra-thin panels to flexible LED strips for architectural and decorative lighting.
2. Smart Lighting and Automation
Modern LEDs can be integrated into smart home systems, offering features such as:
-
Remote control via smartphones and voice assistants.
-
Customizable color temperatures (warm to cool white) for different activities.
-
Automated schedules to improve energy efficiency and convenience.
3. Tunable and Human-Centric Lighting
LEDs allow for circadian lighting systems, which adjust brightness and color temperature throughout the day to support natural biological rhythms. This technology is widely used in workplaces, hospitals, and homes to enhance productivity, relaxation, and sleep quality.
Environmental Impact: How LEDs Are Reducing Energy Consumption
One of the most significant benefits of LED lighting evolution is its impact on energy conservation and sustainability.
-
Lower Energy Consumption: LEDs use up to 80% less electricity than incandescent bulbs, reducing global power demand.
-
Longer Lifespan: With an average lifespan of 50,000 hours, LEDs last 25 times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs, minimizing waste.
-
Reduced Carbon Emissions: By cutting power consumption, LED adoption has helped reduce CO₂ emissions from energy production.
Government initiatives worldwide now encourage or mandate the use of LEDs to combat climate change, making them a key technology in the push for sustainable energy solutions.
The Future of LED Lighting: What’s Next?
The evolution of LED lighting is far from over. As technology advances, new innovations are emerging that promise even greater efficiency, adaptability, and sustainability.
1. Micro-LED and OLED Technology
-
Micro-LEDs offer ultra-thin, high-brightness lighting solutions with better energy efficiency.
-
OLED (Organic LED) lighting provides flexible, paper-thin panels for futuristic applications in interior design and displays.
2. Quantum Dot LEDs (QLEDs)
Quantum dots enhance color accuracy and brightness, making QLEDs a top contender for next-generation LED lighting.
3. Solar-Powered LED Integration
Pairing LEDs with solar panels is becoming increasingly popular in off-grid and renewable energy applications.
4. AI-Driven Adaptive Lighting
Future LED systems will use artificial intelligence (AI) to adjust lighting based on user preferences, weather conditions, and energy demand.
As research and innovation continue, LED lighting will further revolutionize energy efficiency, sustainability, and smart lighting solutions.
LEDs Have Transformed the Lighting Industry
The evolution of LED lighting is one of the most important advancements in modern technology. From its origins in early electroluminescence experiments to its current status as the world’s leading lighting solution, LEDs have consistently improved in efficiency, versatility, and affordability.
As the demand for sustainable, intelligent lighting grows, LED technology will continue to adapt and innovate, shaping the future of energy-efficient lighting worldwide. Whether in homes, offices, public infrastructure, or space exploration, LEDs have become an essential part of modern life—and their journey is far from over.